You don't know who should manage your finances if you're no longer able to make decisions yourself? Are you worried that your medical decisions might be made by someone you didn't choose? Power of attorney is the solution! In this article, you'll learn everything you need to know about creating, using, and understanding the consequences of granting power of attorney. Discover how you can ensure that your affairs are handled by someone you trust and how to prevent abuse. Read on to maintain control over your future!
I. Introduction
Definition and Explanation of Power of Attorney
A power of attorney is a legal document that authorizes one person (the principal) to appoint another person (the agent) to perform specific tasks and make decisions on their behalf. This can be done in various areas such as business matters, finances, real estate, or medical decisions. A power of attorney grants the agent the authority to act on behalf of the principal without the principal needing to be present.
There are different types of powers of attorney. A general power of attorney authorizes the agent to manage all the principal's affairs that are outlined in the power of attorney document. On the other hand, a special power of attorney is limited to certain matters or activities. A power of attorney can also be granted either for a specific time period or indefinitely.
It's important to note the difference between a power of attorney and authorization. Authorization only allows the agent to act and make decisions on behalf of the principal, while a power of attorney also grants the authority to enter into contracts on behalf of the principal.
In Germany, the legal framework for powers of attorney is governed by §§ 184 to 191 of the German Civil Code (BGB). According to § 184 BGB, a power of attorney can be granted either in writing or orally unless the law explicitly requires a written form. It must also be clear what actions the agent is permitted to carry out and which they are not. The duration of the power of attorney and the identity of the agent must also be clearly defined.
What can you do with a power of attorney?
A power of attorney authorizes one person (the agent) to carry out legal transactions on behalf of another person (the principal). The specific powers granted to the agent depend on how the power of attorney is written. Typically, actions such as purchasing, selling, transferring assets, or conducting banking transactions are allowed.
In Germany, a power of attorney can be granted by the principal in accordance with §§ 184 to 193 of the German Civil Code (BGB). The power of attorney must be in writing and meet certain formal requirements to be effective. The agent must also be able to present the power of attorney to third parties to act on the principal's behalf.
How do I grant a power of attorney?
A power of attorney can be granted according to the provisions of the German Civil Code (BGB). The key sections for granting a power of attorney are §§ 184 to 193 BGB.
Here are the steps for granting a power of attorney:
- Form of the Power of Attorney: The power of attorney must be issued in writing and can either be signed by hand or transmitted electronically (e.g., via email).
- Content of the Power of Attorney: It must include the name of the principal and the agent, the scope of the agent’s authority, and the purpose of the power of attorney.
- Validity of the Power of Attorney: The power of attorney must be granted validly, meaning the principal must freely give their consent while observing all relevant legal requirements.
- Transfer of the Power of Attorney: The document must be transferred to the agent, enabling them to present it to third parties and perform the actions specified within
Why is a power of attorney important?
A power of attorney is crucial because it allows the principal to ensure that their affairs are managed by someone they trust if they are no longer able to make decisions themselves. This may occur due to age, illness, accident, or other circumstances.
In business matters, a power of attorney enables the agent to conduct transactions, handle banking matters, and sign contracts on behalf of the principal. This ensures that business operations can continue even if the principal is unable to fulfill their responsibilities.
In financial matters, a power of attorney allows the agent to manage accounts, make investments, and file tax returns on behalf of the principal. This secures the financial well-being of the principal even when they cannot make decisions themselves.
In medical situations, a power of attorney empowers the agent to make decisions regarding medical treatments, care, and housing for the principal. This ensures that the principal’s wishes and interests are respected, even if they cannot make decisions on their own.
In real estate matters, a power of attorney enables the agent to make decisions regarding the management, sale, or rental of properties on behalf of the principal. This ensures that the principal’s interests in their properties are safeguarded even when they cannot act themselves.
Overall, a power of attorney is important because it gives the principal the ability to ensure that their affairs are managed by someone they trust and whose decisions they approve of, should they become unable to make decisions themselves. It offers peace of mind by ensuring that the principal’s wishes and interests are respected even when they cannot act on their own. For the agent, it provides the authority to effectively manage the principal’s affairs. Without a power of attorney, unwanted outcomes could arise, as decisions may be made by individuals not chosen by the principal.
What are the three types of power of attorney?
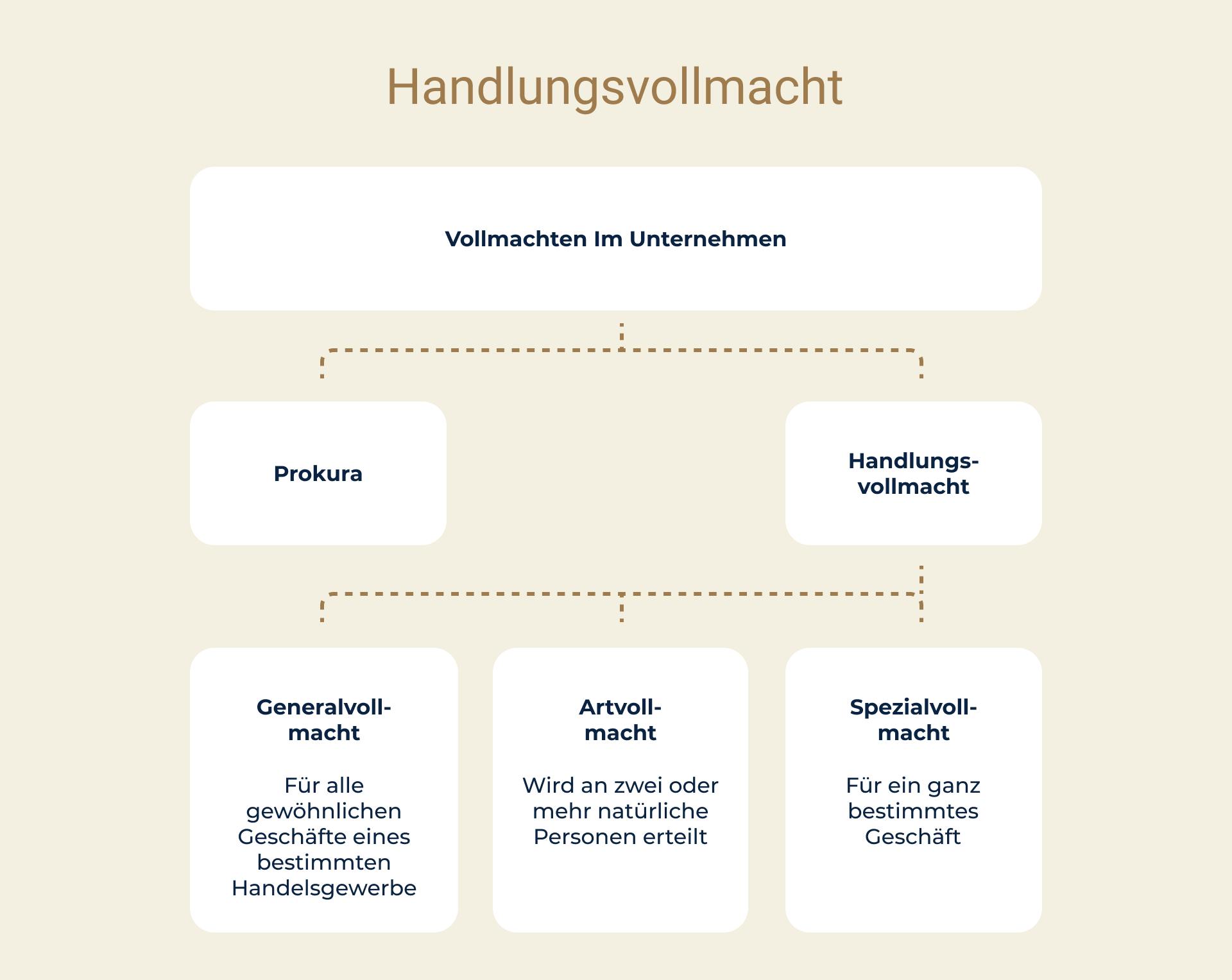
The German Commercial Code (HGB) defines three types of powers of attorney: the general power of attorney, the type-specific power of attorney, and the special power of attorney.
A. General Power of Attorney (Generalhandlungsvollmacht) The general power of attorney, also known as a comprehensive power of attorney, is the most extensive form. It authorizes the agent to carry out almost all relevant legal transactions. This authority closely resembles the Prokura (a formal commercial power of attorney in Germany). The general power of attorney is particularly useful for smaller businesses, as it ensures the smooth continuation of daily operations in the event of the owner's or Prokurist’s (authorized signatory’s) absence.
An example of the application of a general power of attorney would be a hairdresser who is given such authority. This person can conduct all business-related transactions typical for running a hair salon, such as ordering products or supplies. However, they are not allowed to purchase new salon spaces or take out loans.
B. Type-Specific Power of Attorney (Arthandlungsvollmacht) The most common form of power of attorney is the type-specific power of attorney. This authorizes the agent to perform specific legal transactions related to their particular role. Depending on the structure and extent of the authority, a financial limit may be imposed, or it may be restricted to certain types of transactions. This form of power of attorney is often used in areas such as procurement or human resources.
An example of a type-specific power of attorney is in HR. A human resources manager with such authorization may negotiate salaries with job candidates and sign employment contracts, as long as they remain within the company's budget.
C. Special Power of Attorney (Spezialhandlungsvollmacht);In contrast, a special power of attorney is intended for one-time, specific transactions. For example, a marketing employee might be given the authority to sign a contract with an influencer for a particular campaign. Once this specific task is completed, the employee’s authority to act on behalf of the company ends.
It’s important to note that granting a power of attorney comes with great responsibility. To prevent abuse, the scope of the agent's authority must be clearly defined and limited. Powers of attorney should also be regularly reviewed to ensure the agents are still qualified and trustworthy.
The power of attorney is defined in the German Commercial Code (§ 54 Abs. 1 HGB). This law outlines the rights and obligations of agents, including their responsibilities toward business partners and company executives.
What is better: Prokura or Power of Attorney?
Choosing between Prokura (a special commercial power of attorney) and a general power of attorney (Handlungsvollmacht) depends on the specific needs and objectives of the business or individual. Both have their own strengths and weaknesses, and the better option depends on the situation.
A Prokura is a special form of power of attorney that applies exclusively to limited liability companies (GmbH) and public limited companies (AG). With a Prokura, a person is granted the authority to act on behalf of the company and make legally binding declarations. In contrast, a general power of attorney (Handlungsvollmacht) can be issued for any type of legal entity or private individual.
One important advantage of a Prokura is that it is generally easier and faster to issue than a general power of attorney. A Prokura can be granted by the managing director of a GmbH or AG without the approval of the supervisory board or another control body. A general power of attorney, on the other hand, usually requires a written agreement between the principal and the agent, which may take more time to process.
Another advantage of a Prokura is that it is generally more comprehensive than a general power of attorney. A Prokurist usually has the same powers as a managing director and can make decisions that go beyond the scope of a normal power of attorney. A general power of attorney, however, is typically limited to certain tasks or business activities.
A disadvantage of a Prokura is that it carries a higher risk of liability compared to a general power of attorney. Prokurists are liable to third parties for their actions on behalf of the company. In contrast, a general power of attorney applies solely to the agent, who usually does not bear personal liability for actions carried out under the power of attorney.
In summary:
Pros of Prokura:
- Full Authority: Prokura grants the agent the power to conduct all business transactions on behalf of the company, ensuring greater operational freedom.
- Legitimacy: Prokura allows the agent to act as the company's legal representative.
- Easy to Grant: Prokura can be granted easily without complex procedu
- Cons of Prokura:
- 1. Liability: The Prokurist is fully liable for all transactions made on behalf of the company.
- 2. Adherence to Company Policy: The Prokurist must follow company policies and implement the company's decisions.
- Pros of General Power of Attorney (Handlungsvollmacht):
- 1. Limited Authority: The agent's powers are clearly defined, which limits liability.
- 2. Customizable: The power of attorney can be tailored to the specific needs of the company and the agent.
- 3. No Liability for Unauthorized Transactions: The agent is not liable for unauthorized actions outside of their granted powers.
Cons of General Power of Attorney (Handlungsvollmacht):
- Restricted Authority: The agent’s authority is limited to specific tasks, which may reduce flexibility.
- More Complex to Grant: The process of granting a general power of attorney can be more time-consuming and may require notarization.
Difference between Power of Attorney (Vollmacht) and Authorization (Bevollmächtigung)
Although the terms "power of attorney" and "authorization" are often used interchangeably, there is an important distinction between the two.
A power of attorney is a legal document in which one person (the principal) grants another person (the agent) the authority to carry out specific tasks and make decisions on their behalf. This can cover a wide range of areas, such as business matters, finances, real estate, or medical decisions. A power of attorney gives the agent the authority to act on the principal’s behalf, even if the principal is not present.
An authorization, on the other hand, is more limited. It allows the agent to act and make decisions on behalf of the principal but does not grant the authority to sign contracts in the principal’s name. Authorizations can be given verbally or in writing and may not necessarily require a formal legal document.
In summary, a power of attorney provides broader authority than an authorization, as it allows the agent not only to make decisions but also to enter into contracts on behalf of the principal. A power of attorney is therefore more appropriate in situations where the principal cannot manage their own affairs and wants to ensure that someone they trust takes care of those responsibilities.
When is a General Power of Attorney (Handlungsvollmacht) Needed?
I. Business Matters
In the business world, a general power of attorney can be highly significant, as it allows the principal to ensure that their business operations can continue even if they are unable to make decisions themselves. A general power of attorney authorizes the agent to conduct business transactions, manage banking affairs, and sign contracts on behalf of the principal.
A general power of attorney can also ensure that the business continues to operate even if the principal is unable to fulfill their duties due to age, illness, accident, or other circumstances. It is important to define clearly which tasks and decisions the agent is allowed to make in order to avoid misuse. The power of attorney should be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure it aligns with the principal's current needs and wishes. It is also advisable to have the power of attorney notarized or certified by a lawyer to ensure it is legally binding.
For business matters, a general power of attorney can help speed up decision-making and allow the agent to respond efficiently to changing circumstances or emergencies. It also enables the principal to keep their business running even in their absence, for instance, during a business trip or an extended leave.
In summary, a general power of attorney for business matters is a vital tool to ensure that the principal’s affairs are handled properly, even when they cannot make decisions or fulfill their duties. It’s important to carefully plan the power of attorney and select a trustworthy agent to avoid misuse and safeguard the principal's interests.
II. Financial Matters
A general power of attorney for financial matters authorizes the agent to manage financial affairs on behalf of the principal. This can include making investment decisions, conducting banking transactions, filing tax returns, and handling other financial matters.
Such a power of attorney can be particularly useful if the principal is unable to manage their finances due to age, illness, accident, or other circumstances. It also allows the principal to continue managing their finances even when they are not physically present, such as during a business trip or a long absence.
It is crucial to clearly define which financial matters the agent is authorized to handle in order to prevent misuse. Like in business matters, the power of attorney should be reviewed and updated regularly. It is also recommended to have the power of attorney notarized to ensure it is legally enforceable.
A financial power of attorney can facilitate quicker and more efficient decision-making since the agent has the authority to respond promptly to changing financial conditions or emergencies. It is equally important to ensure that the agent has sufficient knowledge and skills in financial matters to carry out their responsibilities responsibly.
In summary, a general power of attorney for financial matters is an essential tool to ensure that the principal's finances are managed properly, even when they are unable to make decisions or manage their own finances. Careful planning is necessary to select a qualified and trustworthy agent to avoid misuse and protect the principal's financial interests.
III.Medical Decisions
A power of attorney for medical decisions authorizes the agent to make decisions regarding medical treatments and care on behalf of the principal. This can include decisions about diagnostic procedures, treatment plans, medications, and moving the principal to a hospital or care facility.
Such a power of attorney is particularly useful when the principal is unable to make decisions due to age, illness, accident, or other circumstances. It allows the agent to make decisions aligned with the principal’s wishes and values, even if the principal cannot express themselves.
It’s essential to clearly define which medical decisions the agent is authorized to make to prevent misuse. The power of attorney should be regularly reviewed and updated to ensure it reflects the current needs and wishes of the principal. Additionally, having the power of attorney notarized or certified by a lawyer ensures its legal validity.
A medical power of attorney can expedite decisions regarding treatment and care, allowing the agent to quickly react to emergencies or changing circumstances. It's also crucial to ensure the agent has sufficient knowledge and skills in medical matters to carry out their responsibilities effectively. The agent must act in line with the principal’s known wishes and values wherever possible.
In some countries or regions, there are legal requirements concerning powers of attorney for medical decisions. It's advisable to research the laws applicable in your area to ensure the power of attorney is legally binding and complies with all necessary requirements.
In conclusion, a power of attorney for medical decisions is an important tool to ensure the principal's healthcare and treatment are managed responsibly when they are unable to make decisions. Careful planning and the selection of a trusted agent are vital to avoiding misuse and safeguarding the principal's interests.
IV. Real Estate Matters
A power of attorney for real estate matters authorizes the agent to make decisions regarding the principal’s real estate properties. This can include decisions about buying, selling, renting, or leasing properties, as well as decisions regarding renovations, maintenance, or other matters related to property ownership and management.
This type of power of attorney can be especially helpful if the principal is unable to manage their real estate due to age, illness, accident, or other circumstances. It also allows the principal to manage their real estate even when they are not physically present, such as during a business trip or extended absence.
It’s important to specify which real estate decisions the agent is allowed to make to prevent misuse. The power of attorney should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect the principal's current needs and preferences. As with other powers of attorney, it's advisable to have the document notarized or certified by a lawyer to ensure it is legally binding.

IV. How is a General Power of Attorney (Handlungsvollmacht) Created?
a. Formal Requirements
Formal requirements refer to the conditions that must be met for a power of attorney to be legally binding. These requirements can vary depending on the country or region, but in most cases, a power of attorney must be in writing and signed by both the principal (Vollmachtgeber) and the agent (Bevollmächtigter). Some countries or regions may also require the document to be notarized or certified by a lawyer to ensure its legal validity.
It’s crucial to ensure that a power of attorney meets the necessary requirements to be considered valid. This usually includes a clear and precise description of the tasks the agent is authorized to perform, as well as the extent of their powers. A power of attorney that is too vague may be deemed invalid.
There are also instances where a power of attorney may not be valid if the principal is incapable of making decisions, for example, due to mental incapacity or impairment. In such cases, the power of attorney may need to be approved by a court to ensure that the principal’s interests are protected.
Another key requirement is that a power of attorney is usually valid for a specific period of time and automatically expires if the principal dies or if the power of attorney is explicitly revoked. The agent must also ensure they act within the timeframe and the authority granted by the principal.
Overall, the formal requirements of a power of attorney are essential for ensuring its legal validity and protecting the principal’s interests. It is important to carefully follow all formal requirements and have the power of attorney notarized or reviewed by a lawyer to ensure it is legally binding.
b. Content of a General Power of Attorney
The content of a general power of attorney refers to the specific tasks and authorities that the agent is permitted to carry out on behalf of the principal. This could include making decisions related to financial matters, medical treatments, real estate, or other affairs. It is essential to clearly describe the content of the power of attorney to prevent misuse and to ensure that the principal’s interests are protected.
A key aspect of the content is that the tasks and authorities of the agent must be precisely defined. For example, the agent may be authorized to make only certain types of decisions, or they may be allowed to act but only within specified limits. It might also be stipulated that the agent can only make decisions under certain circumstances, such as when the principal is unable to make decisions themselves.
It is also important to note that a power of attorney is typically valid for a limited time period, and it automatically expires when the principal dies or if the power of attorney is expressly revoked. The agent must also ensure that they act within the period and authority limits set by the principal.
It is advisable for the power of attorney to include all necessary information, such as the names and contact details of both the principal and the agent, as well as the signatures of both parties. In some cases, it may also be required to have the document notarized or certified by a lawyer to ensure its legal validity.
In summary, the content of a power of attorney is critical to ensuring that it is legally binding and that the principal's interests are safeguarded. Therefore, it is important to carefully consider and define all aspects of the power of attorney to ensure it meets the principal’s needs and wishes.
c. Signature of the Principal and the Agent
The signature of both the principal (Vollmachtgeber) and the agent (Bevollmächtigter) is a crucial component of any general power of attorney (Handlungsvollmacht). The signatures confirm that both parties understand the contents of the power of attorney and agree to its terms.
Typically, the signatures of the principal and the agent must be placed at the end of the document, and both parties should carefully read the document beforehand to ensure that they fully understand all the conditions and requirements. It is also advisable that the signatures of both parties be witnessed or certified by a neutral party to guarantee the legal validity of the document.
In some cases, the signatures may need to be notarized by a lawyer or a notary public to ensure that the power of attorney is legally binding. It is important to remember that a power of attorney is only valid if it is signed by both the principal and the agent.
In summary, the signature of the principal and the agent is a critical element of any power of attorney, as it confirms the legal agreement and consent of both parties and ensures its enforceability.
d. Storage of the Power of Attorney
Proper storage of the power of attorney is vital to ensure that it is accessible when needed. Both the principal and the agent should have a copy of the document, and it should be kept in a secure location.
One option for storing the power of attorney is to place it in a bank safe deposit box or a secure cabinet. It can also be deposited with a lawyer or notary, who can produce the document if required. Another option is to store the document in digital format on a secure USB stick or in cloud storage.
It's also important to note that in some cases, a power of attorney may need to be approved by a court. In such instances, the original document should be filed with the court to ensure that it is available when needed.
In summary, proper storage of the power of attorney is essential to guarantee its availability when required and to prevent misuse. The document should be stored carefully, and both the principal and the agent should ensure that it can be accessed at any time. Additionally, the power of attorney should be reviewed regularly to make sure that it remains up to date and reflects the current needs and wishes of the principal.
Sample General Power of Attorney
Below is a sample template for a general power of attorney, which can be used as a reference.
[Your Name]
[Your Address]
[City, Postal Code]
[Date]
To Whom It May Concern,
I hereby grant Mr./Ms. [Name of the Agent] full power of attorney to act on my behalf in all matters related to [Purpose of the Power of Attorney, e.g., management of my assets].
The agent has the authority to take all necessary actions to conclude these matters, including but not limited to:
[List specific tasks the agent is authorized to perform, e.g., signing documents, negotiating contracts, etc.]
I confirm that Mr./Ms. [Name of the Agent] is authorized to act in my name and on my behalf.
This power of attorney is valid until [Expiration Date or "until revoked"].
Sincerely,
[Your Signature]
[Your Name]
What Happens if a General Power of Attorney (Handlungsvollmacht) is Abused?
i. Criminal Consequences
The abuse or violation of a general power of attorney can lead to criminal consequences. Both the principal and the agent must adhere strictly to the terms of the power of attorney to avoid engaging in illegal activities.
If the agent violates the terms of the power of attorney, for example by misusing the power or making decisions on behalf of the principal that were not authorized, they can be held criminally liable. This could result in serious penalties, such as heavy fines or even imprisonment.
In some cases, the principal could also face criminal liability if they knowingly issue an illegal power of attorney or collaborate in actions that violate the terms of the document.
It's important to note that a power of attorney is only valid within certain legal boundaries, and the applicable laws can vary from country to country. Therefore, both the principal and the agent should ensure that they are familiar with the relevant laws in their jurisdiction and act accordingly.
In summary, both parties must respect the terms of the power of attorney to avoid criminal repercussions and ensure that the principal’s interests are safeguarded.
ii. Civil Consequences
The abuse of a power of attorney can also lead to civil consequences, meaning that either the principal or the agent could be held liable for violating the terms of the agreement.
If the agent breaches the terms of the power of attorney, for example by abusing the authority granted to them or making unauthorized decisions on behalf of the principal, they may face civil liability. This could lead to claims for damages or other financial compensation.
Similarly, the principal could also be held liable in civil court if they knowingly issued an invalid power of attorney or violated the terms themselves.
It is important to note that a power of attorney is only valid within certain legal limits, and the laws governing its use can vary from country to country. Therefore, both the principal and the agent must be familiar with the legal framework in their country and act accordingly.
In some cases, it may also be necessary to have the validity of a power of attorney reviewed by a court to ensure that it was lawfully issued and that it still reflects the current needs and wishes of the principal.
In summary, both the principal and the agent must carefully adhere to the terms of the power of attorney to prevent any civil consequences and to protect the principal's interests. It is also crucial that both parties understand the laws of their country and act accordingly to avoid any legal complications.
How to Revoke a General Power of Attorney: Revocation of a Power of Attorney
A general power of attorney (Handlungsvollmacht) can be terminated for various reasons. According to § 181 of the German Civil Code (BGB), a power of attorney can be revoked at any time, unless there is a specific interest in its continuation. For example, if a business owner grants an employee the authority to conduct transactions with clients but later decides that another person should take over this task, they can revoke the power of attorney at any time.
Another reason a power of attorney may be terminated is upon the death of the principal. According to § 184 BGB, the power of attorney automatically expires upon the principal's death. Therefore, it is advisable to plan in advance and put in place succession arrangements to ensure that business matters continue smoothly after the principal’s death.
Additionally, a power of attorney can also be revoked in the event of the principal’s insolvency. In such a case, the power of attorney becomes invalid, as the company no longer has legal rights, and business operations are taken over by an insolvency administrator.
Finally, a power of attorney may also terminate when the objective of the power of attorney is fulfilled. In such cases, the power of attorney may end automatically or according to a previously agreed condition.
In all cases, it is important to clearly define the conditions for the termination of the power of attorney in advance and be aware of relevant laws to ensure that the power of attorney can be revoked or terminated when needed.
Ways to Revoke a Power of Attorney
The most common way to revoke a power of attorney is through a written declaration by the principal. In this written notice, the principal clearly states that they are revoking the power of attorney and that the agent is no longer authorized to act on their behalf. This written notice should ideally be signed and delivered to both the agent and any third parties affected by the power of attorney, such as business partners or financial institutions.
In cases where there is doubt about the validity of the power of attorney or if the agent is acting against the terms of the document, the principal or concerned parties can seek to have the power of attorney revoked by a court order. A court decision might be necessary if the agent is abusing their authority or if the principal lacks the legal capacity to revoke the document themselves.
The death of the principal.
The principal becoming incapacitated or incompetent, unless the document is specifically a durable power of attorney, which remains in effect in case of incapacity. In these situations, no formal revocation process is required, as the power of attorney expires by law.
It is important for both the principal and the agent to be aware of the available revocation methods and to follow the legal procedures required in their country. Revoking a power of attorney must be done carefully and in a timely manner to prevent any legal complications or unintended consequences.
VI. Conclusion
5 Key Considerations for a General Power of Attorney:
- The creation of a power of attorney should always be done in consultation with a lawyer or notary to ensure that the document is legally valid and comprehensive.
- It is crucial to ensure that the agent is trustworthy and responsible, as they will be acting on behalf of the principal.
- A power of attorney can be granted for various areas, such as finance, real estate, business matters, and medical decisions. It's important to ensure that the power of attorney aligns with the specific needs of the principal.
- A power of attorney can be revoked at any time; however, it's essential to inform all involved parties to avoid legal complications.
- The validity of the power of attorney should be regularly reviewed to ensure it still reflects the current needs and wishes of the principal. A new power of attorney should be issued if circumstances change.
3 Tips for Medical Powers of Attorney:
- Consult with a Doctor: Before creating a medical power of attorney, consult with a doctor to fully understand potential treatments and their implications, ensuring that you make an informed decision.
- Choose a Trusted Person: Ensure that the person you appoint is someone you trust and believe will act in accordance with your wishes and values when making medical decisions on your behalf.
- Keep it Updated: Regularly review and update your medical power of attorney to reflect your current wishes and needs. Inform your doctor and loved ones of any changes so that the right decisions can be made in case of an emergency.
More articles: