Inheritance tax allowances: Everything that is important for 2024
The loss of a loved one is a difficult and stressful time for those left behind. An additional challenge can be the inheritance tax levied on the estate left behind. However, in Germany and many other countries, there are inheritance tax allowances that can help save on taxes.
In this blog article, we will take a closer look at inheritance tax allowances and explain how they can be used. We will examine the amount of inheritance tax and the various allowances in Germany and other countries, and provide practical tips on how to make the most of these allowances.
What is inheritance tax and when does it have to be paid?
Inheritance tax is a tax levied on the assets left behind by a person when they die. It is also known as estate tax. In Germany, inheritance tax is a federal tax levied by the states.
Inheritance tax must be paid when a person dies and their assets are transferred to other persons, known as heirs. The assets left behind include all assets such as real estate, money, stocks, collections, works of art, etc. that the deceased owned during their lifetime.
Not only inheritances, but also gifts and donations made during one's lifetime are subject to inheritance tax if they exceed a certain value. For example, if a house is transferred to children during one's lifetime, inheritance tax must also be paid in this case if the value of the house exceeds the applicable exemption amount.
The amount of inheritance tax is calculated based on the value of the estate left behind and the relationship of the heirs to the deceased. There are different tax rates depending on whether the heirs are close relatives such as spouses, children, grandchildren, etc., or whether they are more distant relatives or strangers.
In Germany, inheritance tax is generally payable as soon as the assets are transferred. However, taxpayers have the option of paying inheritance tax in installments if they apply for this. Inheritance tax must be paid within six months of the inheritance. In certain cases, such as the transfer of business assets, the payment period can be extended to ten years.
What is the Inheritance Tax Act?
The Inheritance Tax Act regulates tax liability for inheritances and gifts in Germany. It is part of tax law and is regulated in the Civil Code (BGB).
Inheritance tax is payable when someone receives an inheritance or gift. The amount of tax payable depends on the value of the inheritance and how closely related the heir or recipient of the gift is to the deceased or donor.
There are various allowances that vary depending on the degree of kinship. For example, there are higher allowances for spouses and children than for more distant relatives or friends.
The amount of inheritance tax depends on the value of the inheritance and the degree of kinship of the heir. There are various tax rates, which can range from 7% to 50%.
However, there are exceptions to tax liability, for example in the case of business assets or inheritances within the family. Gifts made during one's lifetime are also subject to different regulations in some cases.
The amount of inheritance tax: How is the amount of inheritance tax calculated?
The amount of inheritance tax is calculated based on the value of the estate and the relationship of the heirs to the deceased. First, the value of the estate must be determined. This includes all assets such as real estate, money, stocks, collections, works of art, etc. that the deceased owned during their lifetime. The market value of the assets is usually determined by an expert.
The inheritance tax is then calculated based on the value of the estate left behind and the relationship of the heirs to the deceased. For close relatives such as spouses, children, and grandchildren, there are allowances that are exempt from inheritance tax. For more distant relatives and strangers, however, there are no allowances.
The allowances for close relatives and more distant relatives vary depending on the state and are adjusted annually.
It is important to note that inheritance tax is levied on the total value of the estate, even if it exceeds the exemption amount. The tax is therefore not only levied on the portion of the estate that exceeds the exemption amount. For example, if the estate left behind is worth € for close relatives, inheritance tax of € must be paid if no exemption amount is claimed.
How can inheritance tax allowances be used to save on taxes?
Inheritance tax allowances are limits up to which no tax is payable. They are an important tool for saving tax and making inheritance or gifts as cost-effective as possible. In this article, we would like to show you how you can use inheritance tax allowances and what regulations you need to be aware of.
First of all, it is important to know that there are various allowances that depend on the degree of kinship of the heir or donor. For example, there are higher allowances for spouses and children than for more distant relatives or friends. These allowances are offset against the value of the inheritance or gift and can therefore help to reduce the tax burden.
An example: Angela inherits a house worth €500,000 from her father. Angela is single and has no children. She is entitled to an allowance of €20,000. The inheritance tax is therefore calculated on €480,000 (€500,000 minus €20,000 allowance). If Angela were married or had children, the allowance would be significantly higher and the tax burden would therefore be lower.
It is therefore worthwhile to keep a close eye on inheritance tax allowances and, if necessary, take appropriate measures to save on taxes. There are various options available, depending on your individual situation.
One option is to divide the inheritance. If several people inherit jointly, they can divide the value of the inheritance among themselves and thus make optimal use of the tax-free allowance. An example: Mr. Müller leaves his son and daughter a house worth €500,000. Since both children have the same degree of kinship, they could divide the value of the inheritance into €250,000 per person and thus make full use of the €400,000 allowance.
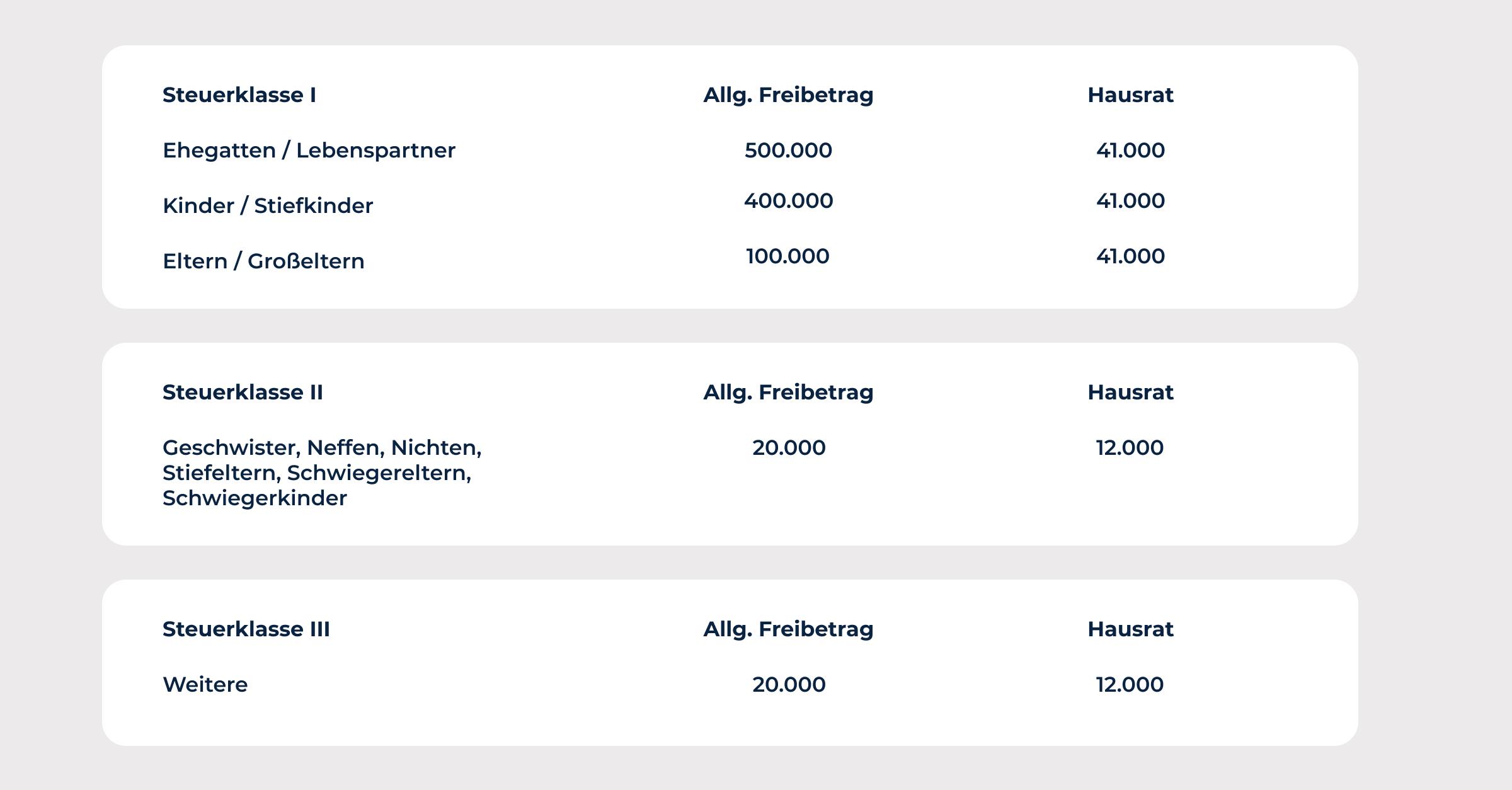
How much can you inherit tax-free?
The amount of the allowances depends on the relationship of the heirs to the deceased and the value of the estate left behind.
There are allowances for close relatives such as spouses, children, and grandchildren that are exempt from inheritance tax. The amount of the allowances for close relatives varies from state to state and is adjusted annually. At the time of writing this answer (December 2021), the allowances for close relatives in most states are €400,000.
However, there are no allowances for more distant relatives and strangers. This means that inheritance tax is levied on the entire value of the estate left behind.
It is important to note that the allowances only apply to the portion of the estate that does not exceed the allowance. For example, if assets worth €500,000 are inherited by a spouse, no inheritance tax is payable because the allowance of €400,000 is exceeded. However, inheritance tax is levied on the portion of the estate that exceeds the exemption amount. In this case, that would be $100,000, which would be taxed at a rate of 7%.
How much inheritance tax do I have to pay for a house?
The amount of inheritance tax payable on a house depends on various factors, such as the value of the house, the relationship of the heirs to the deceased, and the applicable allowances.
A simple example
Let's assume that a son has inherited a house from his parents with a market value of €500,000. The son is the sole heir and therefore a close relative of the parents. In this case, the following allowances apply:
- Up to an allowance of €400,000: 0%
- From €400,000 to €1,400,000: 7%
- From €1,400,000 to €2,400,000: 15%
- Over €2,400,000: 30%
Since the market value of the house is €500,000 and the son is a close relative of the parents, inheritance tax is payable because the exemption limit of €400,000 has been exceeded. In this case, €100,000 is taxed at 7%.
It is important to note that this example is only a general guide and that the amount of inheritance tax is always calculated on an individual basis. The allowances may vary depending on the state and are adjusted annually. It is therefore advisable to consult a notary or tax advisor in the event of an inheritance in order to calculate the exact amount of inheritance tax.
Inheritance tax on real estate
Real estate is an important component of many inheritances and may therefore also be subject to inheritance tax. However, there are exceptions to this tax liability, for example in the case of business assets or inheritances within the family.
The amount of inheritance tax on real estate is based on the market value of the property at the time of inheritance. It is important that the value is determined by an expert to ensure an objective and realistic assessment. The market value is then multiplied by the tax rate, which is based on the degree of kinship of the heir or donor and the value of the inheritance.
It is worthwhile to plan for inheritance tax on real estate early on and, if necessary, take appropriate measures to minimize the tax burden (Gifting real estate). There are various options for doing this, such as dividing the inheritance among several people or gifting it during your lifetime.
Tax rates after deduction of allowances for gifts
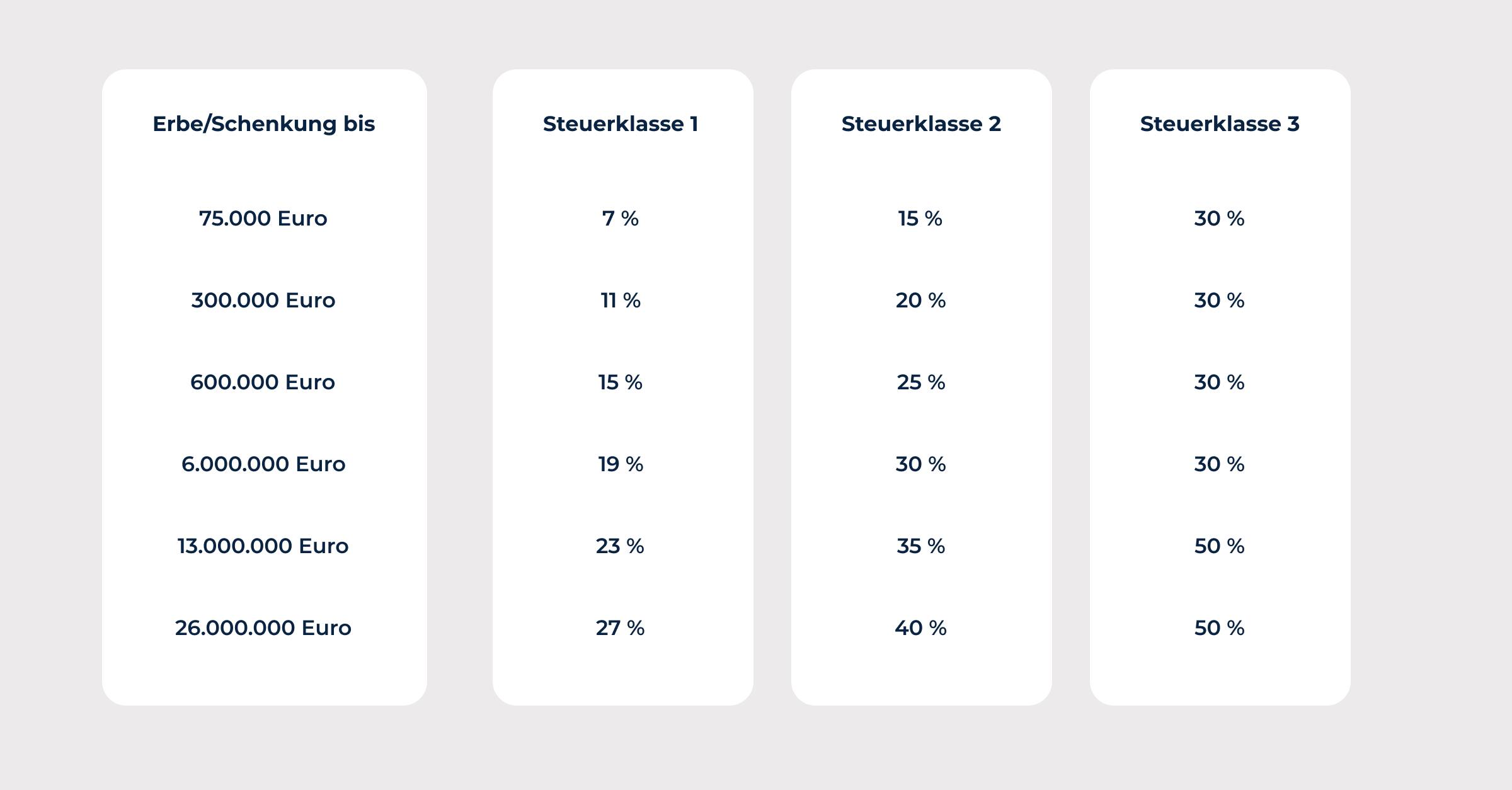
Are there differences in the amount of gift tax and inheritance tax?
Yes, there are differences in the amount of gift tax and inheritance tax. Gift tax is a tax levied on the transfer of assets by gift or bequest.
The amount of gift tax and inheritance tax depends on various factors and can therefore vary from case to case. However, there are some general differences between gift tax and inheritance tax that apply in many countries:
- Tax rate: Gift tax and inheritance tax are generally subject to different tax rates. Gift tax is often lower because it is levied on transfers of assets during a person's lifetime, while inheritance tax is levied on transfers of assets after death.
- Relationship between donor or testator and recipient or heir: The amount of gift tax and inheritance tax varies depending on the relationship between the donor or testator and the recipient or heir. In many countries, lower tax rates or higher allowances apply to transfers between spouses or close relatives.
- Value of the transferred assets: The amount of gift tax and inheritance tax is generally based on the value of the transferred assets. In some countries, there are allowances that mean no tax is payable if the value of the transferred assets is below a certain threshold.
Here is an example to illustrate the differences between gift tax and inheritance tax:
Let's assume that a country has the following regulations for gift tax and inheritance tax:
- Gift tax: A tax rate of 15% applies to gifts of assets between unrelated persons. There is an allowance of €50,000, meaning that no gift tax is payable if the value of the gift is below this threshold.
- Inheritance tax: A tax rate of 25% applies to inheritances of assets between unrelated persons.
When is an inherited house tax-free?
In certain cases, an inherited house may be tax-free, meaning that no inheritance tax needs to be paid. This is the case, for example, if the house is transferred to close relatives such as spouses, children, or grandchildren and the value of the house does not exceed the applicable exemption amount. The exemption amounts for close relatives vary from state to state and are adjusted annually.
There are also exceptions to inheritance tax, known as exemptions. An exemption from inheritance tax may be considered, for example, if the house was used as the main residence and the heir continues to use the house as their main residence within a certain period of time. Another exemption may be considered if the house is transferred to a charitable organization.
It is important to note that exemptions from inheritance tax are narrowly defined and strict conditions must be met. In case of doubt, it is advisable to consult a notary or tax advisor to check carefully whether an exemption from inheritance tax is possible.
Calculating inheritance tax: An example
Inheritance tax is calculated based on the value of the inheritance or gift, with different tax rates ranging from 7% to 50%. The amount of tax depends on the degree of kinship of the heir or donor and the value of the inheritance. Before calculating the tax, allowances are first taken into account, which vary depending on the degree of kinship.
An example: Mr. Müller leaves his daughter Angela a house worth €500,000. Angela is single and has no children. She is entitled to an allowance of €400,000. The inheritance tax is therefore calculated on €100,000 (€500,000 minus €400,000 allowance). The tax rate in this case is 7%.
It is important to note that inheritance tax is not only levied on real estate, but also on other assets such as stocks, cash, or works of art. Business assets and companies may also be subject to inheritance tax under certain conditions. It is therefore worthwhile to familiarize yourself with the regulations at an early stage and, if necessary, seek professional help in order to minimize the tax burden.
Inheritance tax on inherited businesses
When a business is transferred to heirs, inheritance tax is often incurred. However, there are certain exceptions to inheritance tax, known as exemptions, which make it possible to save on taxes.
An exemption from inheritance tax may be considered, for example, if the business was operated as a sole proprietorship or partnership and the heir continues to operate the business within five years (Section 13 (1) No. 2 ErbStG). Another exemption may be considered if the business is transferred to another close relative and the heir continues to run the business for five years (Section 13 (1) No. 3 ErbStG).
It is important to note that exemptions from inheritance tax are narrowly defined and strict conditions must be met. In case of doubt, it is advisable to consult a notary or tax advisor to check carefully whether an exemption from inheritance tax is possible.
How Beglaubigt.de can support you
Beglaubigt.de is an online notary that offers all the services of a traditional notary online. Using state-of-the-art technology and specialized staff, it is possible to create and certify legally binding documents remotely and digitally.
When it comes to inheritance matters, beglaubigt.de can provide particular support in drawing up wills and inheritance contracts. The ability to create these documents online from any location saves time and money. beglaubigt.de also offers the option of completing and submitting inheritance tax returns online.
Overall, beglaubigt.de offers a convenient and legally secure alternative to traditional notaries, which can be particularly advantageous for people who are short on time or unable to visit a traditional notary for other reasons.
More Articles: