What is a real estate donation?
Donation of real estate: An in-depth look at the German Civil Code (BGB). The donation of real estate is a topic that has both legal and tax implications. According to Section 517 of the German Civil Code (BGB), the transfer of ownership of real estate free of charge is defined as a donation.
This legal framework clarifies how and under what conditions property rights can be gifted. It is extremely important to familiarize yourself with these provisions to ensure that a gift is made legally and in accordance with applicable laws.

Section 517 of the German Civil Code (BGB) not only highlights the basic conditions for a real estate gift, but also provides information about the tax consequences that may be associated with such a transaction. Since real estate often represents considerable value, significant tax burdens can arise when it is gifted.
Another important point that is taken into account in the aforementioned paragraph is the need for notarization.
When donating real estate, this is usually unavoidable in order to ensure the legal validity and validity of the transfer.
In the rest of this article, we will take a detailed look at the individual aspects and provisions relating to the donation of real estate, examining the legal and tax implications in more detail.
Why should you give away real estate?
Under certain circumstances, gifting real estate offers significant tax advantages. In Germany, gifts up to a certain allowance are tax-free, and this allowance can be claimed again every ten years. Tax law thus allows significant amounts to be transferred tax-free over a period of time through strategically planned gifts.
Another aspect is the valuation of the property. If a property is gifted at an early stage, the tax valuation is based on the current value of the property. With property prices rising, it may therefore be advantageous to gift a property now rather than bequeath it later at a higher value.
Example: Let's assume that Mr. Müller owns a property that is currently worth €300,000. He is considering gifting this property to his daughter. Since the tax-free allowance for gifts from parents to children is €400,000, the gift would be completely tax-free. However, if Mr. Müller waits ten years and the property increases in value to €500,000 during that time, the difference of €100,000 would be subject to gift or inheritance tax if the property were gifted or inherited at a later date. By gifting the property early, Mr. Müller could therefore avoid potential tax payments.
The tax regulations surrounding gifts are complex, and there are many factors to consider. It is therefore advisable to seek professional advice before making a decision.
1. Requirements for the donation of real estate
Who is permitted to gift real estate?
In principle, anyone who owns real estate can gift it to someone else. To do so, the person must have a valid power of attorney for gifts. This can be issued by a notary and certifies that the person is authorized to gift the real estate.
It is also possible to specify the power of attorney for gifts in a will. In this case, the property can be bequeathed to another person after the owner's death. It is important that the will be certified by a notary so that the power of attorney for gifts is legally valid.
However, donating real estate is not always simple and straightforward. There are various factors to consider before donating real estate. For example, it is important that the donor actually owns the property and that it is not subject to a lien. Otherwise, the donation could be invalid.
It is also important for the donor to consider the financial consequences of the gift. Donating real estate can have tax implications. As a rule, gifts to people close to the donor, such as family members, are monitored by the tax authorities.
What formalities must be observed?
When donating real estate, there are numerous formalities to be observed. These serve not only to make the donation legally effective, but also to prevent possible disputes in the future. In the following, we will discuss the essential formalities:
Notarization: One of the most important formalities when donating real estate is notarization. This means that the donation agreement must be notarized by a notary. The notary verifies the identity of the contracting parties, informs them of the legal consequences, and ensures that all parties understand the contract and its implications. Without notarization, the donation of real estate is not valid in Germany.
Entry in the land register: In order for the gift to be recognized in legal transactions, the transfer of ownership must be entered in the land register. To this end, the notary submits an application to the relevant land registry office. Only upon entry in the land register does the recipient officially become the owner of the property.
Land registry fees: Fees are charged for registration in the land registry, which may vary depending on the state and the value of the property.
Submission of the gift agreement to the tax office: The gift of real estate can have tax consequences. It is therefore necessary to submit the gift agreement to the relevant tax office, which will then decide on any gift tax that may be payable.
Possible exemption from real estate transfer tax: For gifts between certain relatives (e.g., between parents and children), an exemption from real estate transfer tax can be applied for. It is advisable to seek advice from a tax advisor on this matter.
Register of encumbrances and contaminated sites: It is advisable to consult the register of encumbrances and contaminated sites before making a gift. This allows both parties to ensure that there are no unexpected encumbrances or obligations associated with the property.
Obtaining permits: In some cases, it may be necessary to obtain certain permits, e.g. if the property is listed as a historic building or is located in a specific development area.
Deed of gift for real estate
A deed of gift for real estate gifts is an important document used when transferring real estate from one person to another. This type of deed of gift is usually issued by a notary and contains all relevant information about the property being gifted and the persons involved.
A deed of gift for real estate gifts will generally contain the following information:
- The names and addresses of the persons involved, i.e., the donor and the recipient
- The full address of the property being gifted
- A detailed description of the property, including its size, number of rooms, and year of construction.
- A list of all encumbrances and restrictions on the property, such as land charges or usufructuary rights.
- Confirmation that the donor has unrestricted ownership of the property and is entitled to gift it.
- A declaration by the donor that he is donating the property of his own free will and without consideration.
- A statement from the recipient confirming that they accept the gift and that they are aware of any encumbrances and restrictions on the property.
2. Gift tax allowances
When is the donation of real estate tax-free?
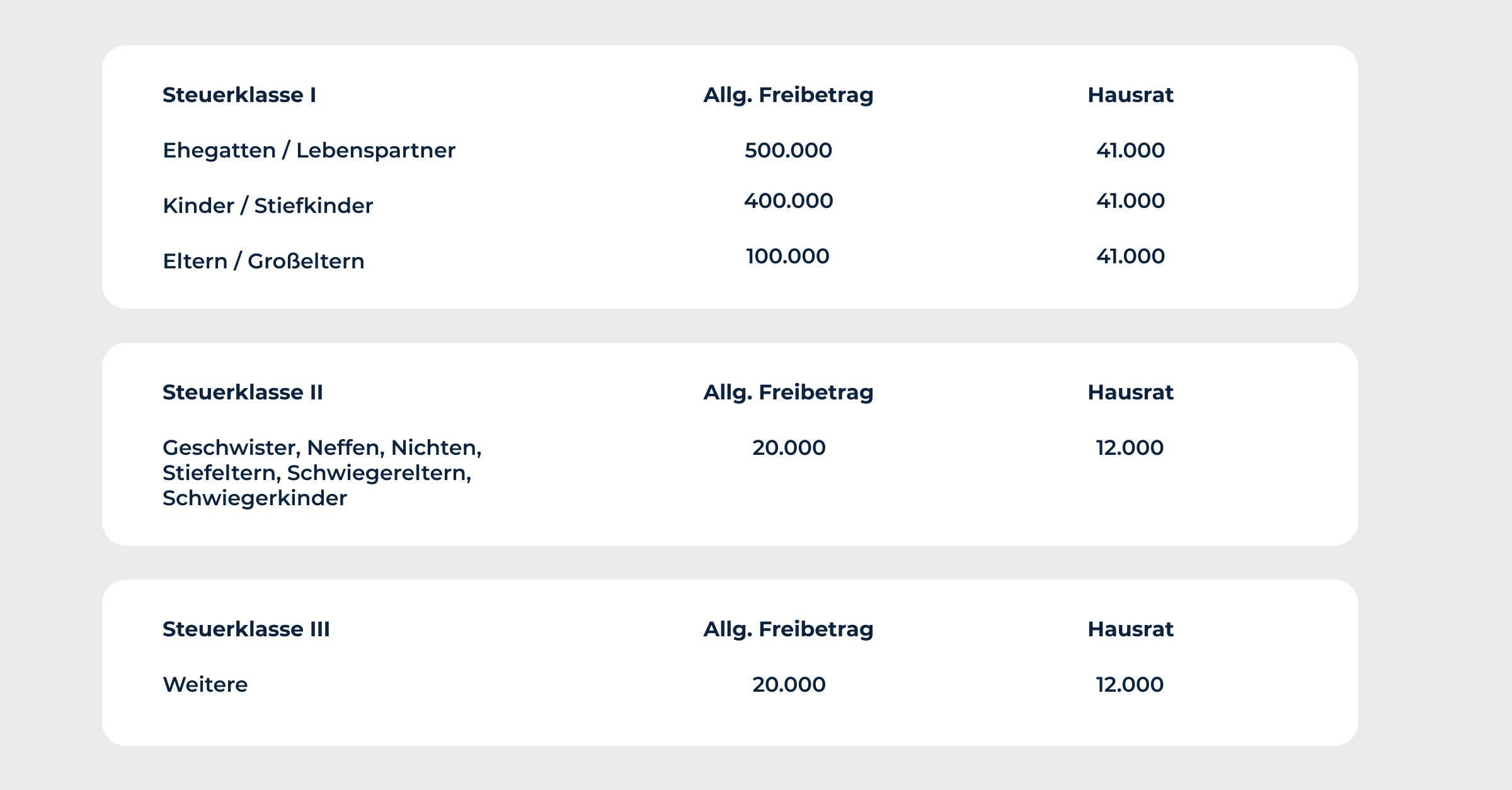
Inheritance tax and tax brackets for real estate gifts
Inheritance tax is a tax that may be levied on the transfer of assets when someone dies. This tax may also be levied on the transfer of real estate, especially if the value of the property exceeds the applicable exemption amount.
The allowance is the amount up to which no inheritance tax is payable. In Germany, the allowance is currently €500,000 for children, grandchildren, and spouses, and €20,000 for other heirs. If, for example, the value of the property is €600,000, inheritance tax of €100,000 would be payable, as the exemption amount of €500,000 has been exceeded.
However, the amount of inheritance tax depends not only on the value of the property, but also on the tax class of the heir. In Germany, there are six tax classes based on the degree of kinship of the heir and the value of the inheritance. Tax class I applies, for example, to spouses and children, while tax class VI applies to more distant relatives and other heirs. The amount of inheritance tax can vary depending on the tax class.
It is important that heirs find out about any inheritance tax that may be payable before taking over a property in order to avoid unpleasant surprises.
In Germany, the donation of real estate is subject to gift tax (see also: Inheritance tax allowances). However, there are allowances and certain exceptions that, if complied with, mean that the gift remains tax-free. The exact allowances may change over time, and it is always advisable to consult the current legal regulations and the relevant tax laws. At the time of my last training (until January 2022), the following regulations apply:
Exemptions per donor and recipient:
- Spouses and registered partners: €500,000
- Children and stepchildren: €400,000
- Grandchildren: 200,000 euros
- Great-grandchildren and others: 100,000 euros
- All other persons (e.g., friends, non-relatives): 20,000 euros
For example, if parents gift a property to a child and the value of the property is less than €400,000, no gift tax is payable. The same applies to other situations, as long as the value of the property does not exceed the respective allowance.
Further tax benefits:
- Family home: Under certain conditions, the gift of a family home from parents to children may be tax-free if the child immediately uses the property themselves and continues to do so for a period of at least ten years.
- Business assets: When donating business assets, which may also include rented real estate, tax benefits or exemption rules apply under certain conditions.
Important to note:
- The allowances can be claimed again every ten years.
- If the value of the property exceeds the applicable allowance, only the excess amount is taxable.
- It may be advisable to spread the gift over several years or to different people in order to make optimal use of the tax allowances.
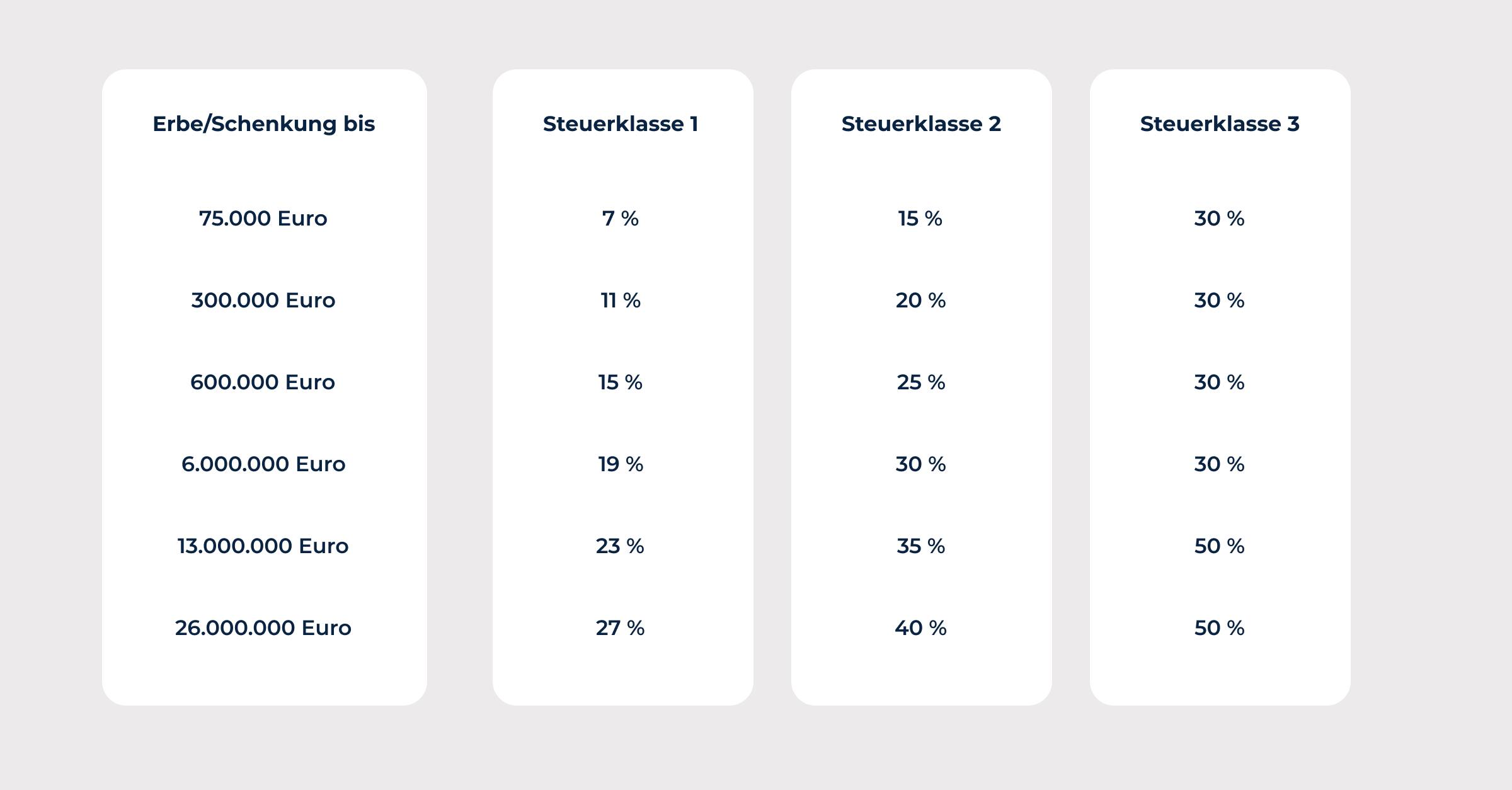
How much does it cost to transfer ownership of a house?
Transferring ownership of a house when donating real estate can be costly in some circumstances, as it involves various fees and taxes.
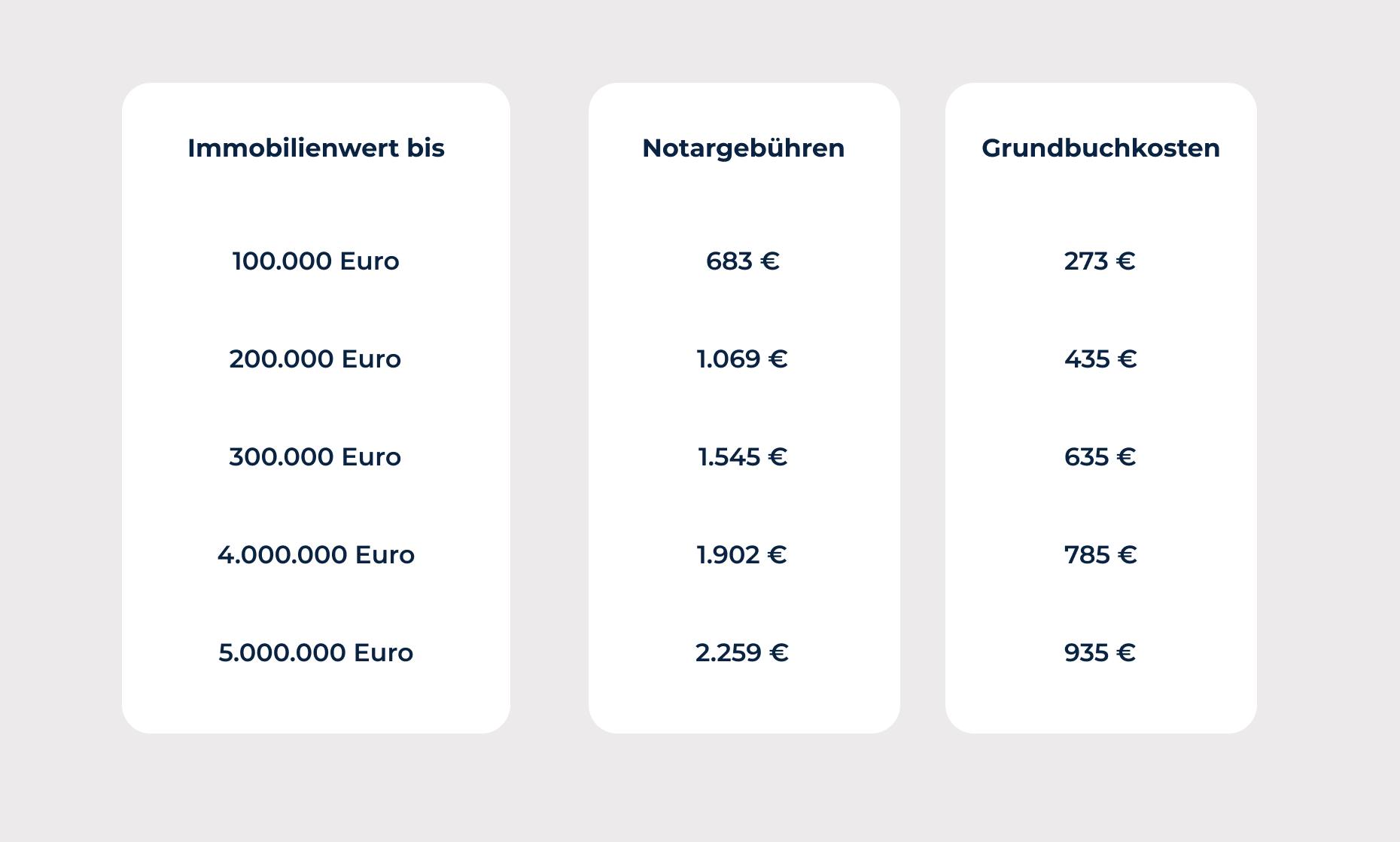
According to Section 97 of the GNotKG (Law on Notary Fees and Monetary Compensation for Lawyers), notary fees are payable for the notarization of a real estate donation. These are calculated based on the value of the property and may vary depending on the federal state. In addition, fees may also be incurred for registering the new owner in the land register, which also depend on the value of the property.
In addition, in many cases, gift tax must also be paid when real estate is gifted. According to § 46 GNotKG, this is paid by the recipient and is based on the value of the property and the relationship between the donor and the recipient. The closer the relationship, the lower the tax; in some cases, it may even be waived entirely for close relatives.
When is the best time to gift a property?
The best time to gift a property depends on various factors and can vary from case to case. One important factor is the financial situation of the donor and the recipient. If the donor is in financial distress and needs the property to meet their own financial obligations, then it is probably not the right time to make a gift.
Another important factor is the tax situation. In Germany, there are certain allowances and tax rates for gifts, which depend on the relationship between the donor and the recipient and the value of the property. It may be advisable to make the gift at a time when the tax burden for the donor and the recipient is as low as possible.
Another important factor is the family situation. If, for example, the donor still has minor children who would receive nothing from a gift, it may make sense to make the gift at a time when all children are of legal age and can benefit from it.
4. Tips for planning the donation of real estate
Which is better: a gift or a transfer of ownership?
A gift and a transfer of ownership are both ways of transferring possession of something to someone else. Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages, and which method is better depends on the circumstances.
A gift is a voluntary transfer of property without consideration. The gift can be made either during the donor's lifetime or through a will after the donor's death. One advantage of a gift is that it may be tax-privileged. However, the donor must always make the gift voluntarily and cannot take it back once it has been made.
A transfer, on the other hand, is the transfer of ownership by means of a formal contract. Unlike a gift, a transfer does not qualify for tax relief. However, one advantage of a transfer is that it can be reversed as long as both parties agree.
Overall, therefore, the most suitable method depends on the circumstances and preferences of the parties involved. When it comes to tax benefits, a gift may be the better choice.
Deed of gift for the donation of real estate
A gift agreement is a contract concluded between two parties for the transfer of assets, such as real estate. This contract stipulates that the asset, in this case the real estate, is gifted by one person, the donor, to another person, the recipient.
This contract can be concluded voluntarily or under duress and must meet certain formal legal requirements in order to be legally valid. (Further information: Gift agreement: what to consider)
A gift agreement for the donation of real estate (see also: Gift Agreement Template) can be concluded for various reasons. A common reason is the transfer of ownership of a house or apartment from parents to their children. In this case, the gift agreement can serve to regulate the transfer of ownership and prevent the property from only passing to the children after the parents' death, which would result in them being burdened with inheritance taxes.
A gift agreement for the donation of real estate must always be in writing and notarized. This agreement lists all relevant information about the property, such as its exact location, the type of building, and the size of the plot of land. The agreement should also specify whether the property is a condominium or a single-family home and whether it is a developed or undeveloped plot of land.
A gift agreement for the donation of real estate should also contain provisions regarding who is responsible for any debts if the property has been encumbered in the past.
What is the difference between gift tax and inheritance tax?
Gift tax is a tax levied on money or other assets transferred from one person (the donor) to another person (the recipient) as a gift. Gifts can be made during the donor's lifetime or upon their death. In Germany, gift tax is determined and levied by the federal state in which the donor resides.
Inheritance tax is a tax levied on the estate of a deceased person. It is payable by the heirs and levied by the state in which the deceased last resided. Inheritance tax is levied on the inheritance or acquisition of assets by the heir.
Unlike gift tax, which is paid during the lifetime of the donor, inheritance tax is only payable after the death of the deceased. The amount of inheritance tax depends on various factors, such as the value of the estate and the relationship between the deceased and the heirs.
An example makes it clearer
Let's assume that a married couple has a house worth €500,000 and wants to transfer it to their son. The couple lives in Bavaria, where the tax rate for gifts between parents and children is 5%. In this case, the gift tax would amount to €25,000 (€500,000 x 5%).
If the couple decides instead to bequeath the house in a will, the inheritance tax would only become due after the couple's death. In Bavaria, the tax rate for inheritances between parents and children is also 5%. So if the couple both die within 10 years, the inheritance tax would also be €25,000. However, if the couple survives for more than 10 years, the tax rate would increase to 7% and the inheritance tax would be €35,000.
In this example, it would therefore be more financially advantageous for the couple to gift the house during their lifetime, as the gift tax is lower than the inheritance tax that would be payable if they were to bequeath the house in a will. However, it is important to note that this is only an example and that the tax rates and allowances for gift tax and inheritance tax may vary from state to state. It is therefore advisable to seek advice from a tax advisor or lawyer if you have any questions about these taxes.
Summary key points at a glance
- Donating real estate enables asset transfer during one's lifetime
- Significant tax advantages through strategic gifting
- It is essential to take into account the current and future value of the property.
- Donations have long-term, irreversible consequences.
- Thorough planning and comprehensive advice are essential.
More Articles: