I. Introduction
Definition: What is property tax?
Property tax is a levy imposed on the ownership of land. It finances the general tasks of local authorities, such as schools, roads, and public facilities. The amount of property tax is calculated based on the value and use of the land.
In Germany, property tax is regulated by Section 1 of the Property Tax Act (GrStG). According to this, municipalities have the right to levy a tax on the use of land and buildings. The amount of property tax is determined by the assessment rate, which each municipality sets itself, meaning that property tax can vary from municipality to municipality.
There are two types of property tax: property tax A and property tax B. Property tax A is levied on agricultural and forestry land and is based on its utility value. Property tax B is levied on all other land and is based on its unit value, which is calculated from the market value of the land and the value of the buildings on it.
In Germany, all owners of land and buildings are required to pay property tax, regardless of whether they use the land or building themselves or rent it out. However, certain properties and buildings, such as churches, museums, and accommodation for asylum seekers, are exempt from property tax.
Property tax is levied by the tax authorities. Each year, a property tax assessment notice is sent out, specifying the amount of property tax for the coming year. This assessment may change due to changes to the property or its use. Owners can appeal against the property tax assessment. Property tax is usually payable quarterly and must be paid within two months of receiving the assessment. There are various payment methods, such as direct debit or direct debit authorization. Timely payment is important to avoid reminder fees and interest.
In Germany, there are regular discussions about the amount and calculation of property tax. Critics consider it unfair because it depends not only on the value of the property but also on its use. Others see it as an important source of income for municipalities and as a fair way to finance public services. Nevertheless, there are repeated efforts to reform and simplify the property tax system.
Why is property tax important?
Property tax is an important source of revenue for municipalities and thus contributes to the financing of public services. These include, for example, schools, roads, public facilities, and services. Without property tax, municipalities would have to rely on other sources of revenue to fulfill these tasks.
Property tax is also important for ensuring a fair distribution of burdens within the community. It ensures that those who benefit from public services also make a corresponding contribution. For example, homeowners who benefit from well-developed roads and schools also contribute to their financing.
In addition, property tax is an important source of revenue for the state. The collection of property tax generates tax revenue, which in turn can be used for the federal budget. Property tax thus also contributes to the financing of tasks that go beyond the municipalities, such as defense or social services.
Overall, property tax is therefore an important factor in financing public services and ensuring a fair distribution of burdens within municipalities and the federal government.
How is property tax calculated?
Factors that influence the amount of property tax (e.g., value of the property, location, etc.)
Property tax is calculated based on the value of the property and its use. There are two types of property tax: property tax A and property tax B.
Property tax A is levied on agricultural and forestry land and is based on its utility value. This in turn depends on the type of use of the land, for example whether it is used for agriculture or forestry.
Property tax B is levied on all other properties and is based on their unit value, which is derived from the market value of the property and the value of the buildings on it. The market value of the property is in turn determined on the basis of various factors, such as the size, location, and condition of the property. The value of the buildings on the property is also taken into account.
In addition to these factors, the municipality's assessment rate can also influence the amount of property tax. The assessment rate is the percentage by which the property tax is increased and is determined by each municipality itself.
As an example
Assuming that the property has a market value of €500,000 and there are buildings on it worth €300,000. The municipality's assessment rate is 500%. Then the property tax B for this property would be calculated as follows: (€500,000 + €300,000) * 500% = €1,400,000 * 500% = €7,000. Property tax A, on the other hand, would only be calculated for agricultural and forestry properties and would be based on the value in use rather than the unit value.
Calculation formula for property tax
The calculation formula for property tax B is as follows:
Property tax B = (market value of the land + value of the buildings on it) * municipal assessment rate
The calculation formula for property tax A, on the other hand, is as follows:
Property tax A = Usable value of the property * Municipal assessment rate
To take up the previous example: Let's assume that the property has a market value of €500,000 and that there are buildings on it worth €300,000. The municipality's assessment rate is 500%. Then the property tax B for this property would be calculated as follows:
Property tax B = (500,000 euros + 300,000 euros) 500% = 1,400,000 euros 500% = 7,000 euros
Property tax A, on the other hand, would only be calculated for agricultural and forestry land and would be based on the utility value rather than the standard value.
Calculation formula for property tax
The calculation formula for property tax B is as follows:
Property tax B = (market value of the land + value of the buildings on it) * municipal assessment rate
The calculation formula for property tax A, on the other hand, is as follows:
Property tax A = Usable value of the property * Municipal assessment rate
To take up the previous example: Let's assume that the property has a market value of €500,000 and that there are buildings on it worth €300,000. The municipality's assessment rate is 500%. Then the property tax B for this property would be calculated as follows:
Property tax B = (500,000 euros + 300,000 euros) * 500% = 1,400,000 euros * 500% = 7,000 euros
Property tax A, on the other hand, would only be calculated for agricultural and forestry land and would be based on the utility value rather than the standard value.
Changes to the leverage ratios
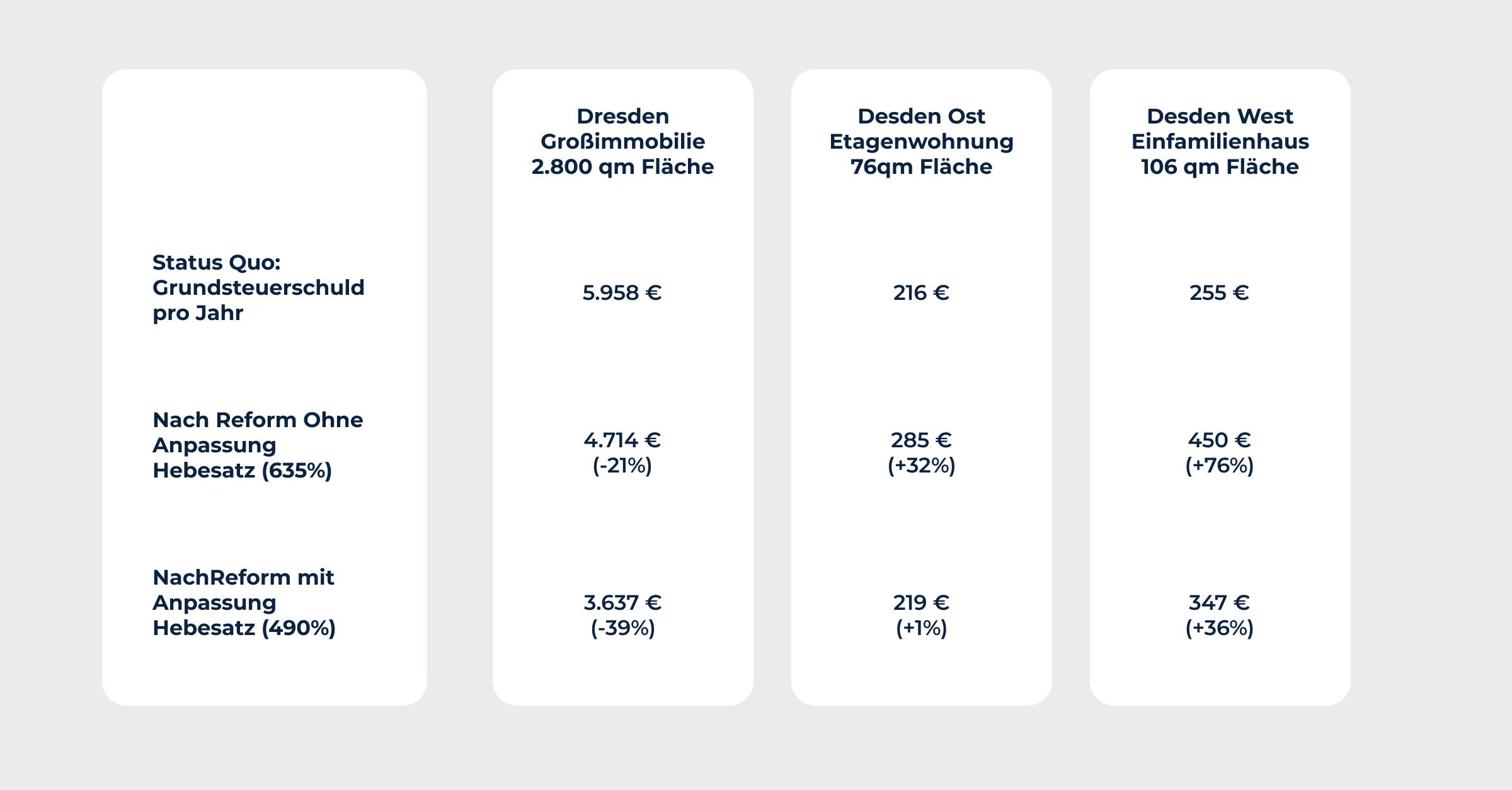
The Taxpayers' Association of North Rhine-Westphalia fears that property tax could increase in around 60% of the state's cities and municipalities next year. The reason for this is that on December 20, the North Rhine-Westphalia state parliament passed the 2023 Municipal Financing Act, which creates the conditions for extensive tax increases.
In Rhineland-Palatinate, the levelling rates for property tax and trade tax are also being increased, which many municipalities are following suit. There are also increases in Hesse, such as in the municipality of Oberursel, where property tax B has been raised from 750 to 947 points, or in Lampertheim in the Bergstraße district, where property tax B has risen from 460 to 580 points and property tax A (for farmers and forestry businesses) from 330 to 430 points.
In the Hochtaunus district, property tax A and B have risen from 450 to 595 points and trade tax from 357 to 400 points. However, there are also municipalities that have not been able to push through their plans for increases, such as Hohenstein in the Rheingau-Taunus district, whose municipal parliament rejected the planned increase in property tax B from 735 to 1135 points and trade tax from 380 to 500 points.
In Lower Saxony, the Taxpayers' Association expects rising rates for property and trade tax, and according to a survey by consulting firm EY, 35% of municipalities in the state are planning to do so, including the state capital Hanover, with a jump from 600 to 700 points as of January 1, 2024. In Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, citizens in Rostock, Ribnitz-Damgarten, and Neubukow must prepare for higher costs. So far, there are no known reports of property tax increases in Hamburg, Baden-Württemberg, Bavaria, Saarland, and Schleswig-Holstein.
III. The property tax assessment notice
What is a property tax assessment?
A property tax assessment is a letter that specifies the amount of property tax for the coming year. It is sent by the tax office and is considered a binding payment request. The property tax assessment is issued each year and may change due to changes in the property or its use.
The property tax assessment notice usually contains the following information:
- the amount of property tax for the coming year
- the period for which the property tax applies (e.g., January to December)
- the date on which the property tax is due (e.g., quarterly)
- the account number or bank details to which the property tax can be transferred
- If applicable, a direct debit authorization or direct debit procedure for collecting property tax.
It is important to read the property tax assessment carefully and, if necessary, check whether the calculated property tax is correct. If the owner disagrees with the property tax assessment, they can lodge an objection and explain their point of view. They have two months after receiving the property tax assessment to do so. The objection can be submitted to the tax office or the competent local court.
It is important that property tax is paid on time, as otherwise reminder fees and interest may be incurred. Property tax is usually payable quarterly and must be paid within two months of receiving the property tax assessment notice. There are various ways to pay property tax, such as direct debit or direct debit authorization.
Revaluation of all properties in Germany
In Germany, a revaluation of real estate is currently underway. This means that all properties in the federal territory will be revalued and the unit values used to calculate property tax will be adjusted.
The revaluation takes place every 15 years and is part of the so-called Valuation Act. The last time the properties were revalued was in 1964, which is why the revaluation is now due. The revaluation is intended to adjust the unit values to current market prices and thus achieve a fairer assessment of property tax.
The revaluation is carried out by the competent valuation authorities and is generally free of charge for property owners.
Who can use the "Property Tax Return for Private Property"?
The "Property Tax Return for Private Property" is a form that can be used by owners of private land to calculate the property tax for their land. This form is usually available from the relevant tax office or municipality and can also be downloaded online from the relevant websites.
In order to use the "Property Tax Return for Private Property," the owner must provide the following information:
- Size of the property
- Land register number (if available), district, parcel, parcel number
- For condominiums: co-ownership share of the property
- Tax number/file number of the property
- standard land value
- Exact year of construction of the building (from 1949 onwards)
- Living space of the property
- Number of garage parking spaces
- Contact details of the owners and their shares in the property.
The owner can use this information to calculate the property tax for their land. It is important that the information is correct and complete, otherwise the calculated property tax may be incorrect.
The "property tax return for private property" is not usually a binding property tax assessment and serves only as a guide for the owner. The final property tax assessment is issued by the tax office or the municipality and takes into account all relevant factors that influence the amount of property tax. The property tax assessment is binding for the owner and must be paid by them unless an objection or appeal is lodged.
When is a property tax assessment notice sent out?
A property tax assessment notice is usually sent out every year. It is issued by the tax office responsible for collecting property tax in the municipality. The property tax assessment notice is usually sent out during the year to which it applies. The exact date on which the property tax assessment notice is sent out depends on the respective tax offices and may therefore vary from municipality to municipality.
However, the property tax assessment is usually sent out as early as possible so that the owner has enough time to pay the property tax. It is important that the property tax is paid on time, as otherwise reminder fees and interest may be incurred. Property tax is usually due quarterly and must be paid within two months of receiving the property tax assessment.
Who sends out property tax notices?
The property tax assessment notice is sent by the tax office responsible for collecting property tax in the municipality. In Germany, there are various tax offices responsible for collecting taxes. Which tax office is responsible for collecting property tax in a particular municipality depends on the location of the municipality and the relevant tax office district.
The property tax assessment is issued by the tax office and then sent to the owner of the property. The property tax assessment is considered a binding payment request and usually contains information on the amount of property tax, the period for which it applies, and the date on which it is due. It is important to read the property tax assessment carefully and, if necessary, check whether the calculated property tax is correct.
Where can I obtain the property tax assessment notice?
The property tax assessment notice is sent by the tax office responsible for collecting property tax in the municipality. It is usually sent by post to the owner of the property. If the owner of the property is unknown or has no postal address, the property tax assessment notice may also be posted on the property.
What does a property tax assessment notice contain?
A property tax assessment notice usually contains the following information:
- The amount of property tax for the coming year: The property tax assessment notice contains the amount of property tax that the owner of the property must pay in the coming year. Property tax is calculated based on the value of the property and its use. There are two types of property tax: property tax A and property tax B. Property tax A is levied on agricultural and forestry properties and is based on their utility value. Property tax B is levied on all other properties and is based on their unit value, which is derived from the market value of the property and the value of the buildings on it.
- The period for which the property tax applies: The property tax assessment notice specifies the period for which the property tax applies. As a rule, property tax applies for a calendar year, i.e. from January to December.
- The date on which property tax is due: The property tax assessment notice specifies the date on which property tax is due. Property tax is generally due quarterly and must be paid within two months of receiving the property tax assessment notice.
- The account number or bank details to which the property tax can be transferred: The property tax assessment notice contains the account number or bank details to which the property tax can be transferred. The owner usually has various options for paying the property tax, such as direct debit or direct debit authorization.
- If applicable, a direct debit authorization or direct debit procedure for collecting property tax: Some tax offices offer property owners the option of using a direct debit authorization or direct debit procedure to collect property tax. In this case, the property tax is automatically debited from the specified account without the property owner having to take any action.
IV. Objection to the property tax assessment
Reasons for an objection (e.g., incorrect calculation, unjustifiably high tax)
There are various reasons why the owner of a property may appeal against a property tax assessment. Here are a few examples:
- Incorrect calculation: The owner can lodge an objection if they believe that the calculated property tax is incorrect. In doing so, they can refer, for example, to changes in the property or its use that should result in a different property tax calculation.
- Unjustifiably high tax: The owner can lodge an objection if they believe that the property tax is unjustifiably high. In doing so, they can refer, for example, to comparable properties in the vicinity whose property tax is significantly lower.
- Incorrect information in the property tax assessment: The owner can lodge an objection if the property tax assessment contains incorrect information, such as incorrect property areas or incorrect types of use.
- No knowledge of the use of the property: The owner can lodge an objection if he was unaware of the use of the property and was therefore unable to pay the property tax. In this case, however, they must prove that they had no knowledge of the use of the property and that they did everything in their power to obtain knowledge of the use.
It is important that the owner clearly states in the objection why they believe the calculated property tax is incorrect and what changes they would like to see. They should refer to facts and evidence and, if necessary, attach documents such as floor plans or usage agreements. After the objection has been submitted, the tax office or local court will review the case and decide whether the property tax has been calculated correctly or whether it needs to be adjusted. The owner will be informed of the outcome and will have the opportunity to appeal the decision if necessary.
How do I file an objection to the property tax assessment?
If the owner disagrees with the property tax assessment, they can lodge an objection and present their view of the matter. They have two months from receipt of the property tax assessment to do so. The objection can be submitted to the tax office or the competent local court.
To file an objection, the owner must usually fill out a form and explain why they disagree with the amount of property tax. For example, they can refer to changes in the property or its use that should result in a different property tax calculation.
The objection can be submitted in writing or verbally. If the objection is submitted verbally, it must generally be confirmed in writing. It is advisable to submit the objection in writing, as this ensures greater traceability.
After the objection has been submitted, the tax office or local court will review the case and decide whether the property tax has been calculated correctly or whether it needs to be adjusted. The owner will be informed of the outcome and will have the opportunity to appeal the decision if necessary.
V. Payment of property tax
When is property tax due?
As a rule, property tax is due quarterly and must be paid within two months of receiving the property tax assessment notice. This means that property tax is due in four installments, each amounting to one quarter of the total amount. The exact due dates are specified in the property tax assessment notice and may vary depending on the tax office and municipality.
It is important that the owner pays the property tax on time, as otherwise interest and reminder fees may be incurred. If the owner is unable to pay the property tax for financial reasons, they may be able to apply for a deferral or waiver. To do so, they must contact the tax office or local court and explain their financial situation.
Payment options (e.g., direct debit, direct debit authorization)
The owner usually has various options for paying property tax, such as:
- Bank transfer: The owner can transfer the property tax to the account specified in the property tax assessment notice. To do this, they need the account number and the name of the recipient, which is usually the tax office or the municipality.
- Direct debit: Some tax offices offer property owners the option of using direct debit to collect property tax. In this case, the property owner grants the tax office or municipality a direct debit authorization stating that the property tax may be debited from the specified account. The direct debit procedure has the advantage that the owner does not have to take any action themselves and the property tax is automatically debited from the account.
- Direct debit authorization: Some tax offices offer property owners the option of using a direct debit authorization to collect property tax. In this case, the property owner grants the tax office or municipality a direct debit authorization stating that the property tax may be debited from the specified account. The direct debit authorization has the advantage that the owner does not have to take any action themselves and the property tax is automatically debited from the account.
Important links for each federal state for the assessment
In Germany, each federal state has its own valuation authority responsible for the revaluation of land. The following links lead to the relevant valuation authorities in the individual federal states:
- Baden-Württemberg: https://www.bewertung.baden-wuerttemberg.de/
- Bavaria: https://www.bewertung.bayern.de/
- Berlin: https://www.berlin.de/sen/finanzen/steuern/bewertung/
- Brandenburg: https://www.bewertung.brandenburg.de/
- Bremen: https://www.bewertung.bremen.de/
- Hamburg: https://www.bewertung.hamburg.de/
- Hesse: https://www.bewertung.hessen.de/
- Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania: https://www.bewertung.mecklenburg-vorpommern.de/
- Lower Saxony: https://www.bewertung.niedersachsen.de/
- North Rhine-Westphalia: https://www.bewertung.nordrhein-westfalen.de/
- Rhineland-Palatinate: https://www.bewertung.rheinland-pfalz.de/
- Saarland: https://www.bewertung.saarland.de/
- Saxony: https://www.bewertung.sachsen.de/
- Saxony-Anhalt: https://www.bewertung.sachsen-anhalt.de/
- Schleswig-Holstein: https://www.bewertung.schleswig-holstein.de/
- Thuringia: https://www.bewertung.thueringen.de/
Owners can find further information on the revaluation of properties in their state, such as deadlines and forms, on the websites of the valuation authorities. It is advisable to visit the websites of the valuation authorities regularly to stay up to date and not miss any deadlines.
VI. Conclusion
Summary of the most important information about property tax and the property tax assessment notice
Property tax is a tax levied on the ownership of land. It is an important source of revenue for the public sector and is used to finance public services such as road construction and schools. The amount of property tax is calculated based on the assessed value of the property, which is reassessed every 15 years. The owner of the property receives a property tax assessment notice, which contains the amount of property tax and the due dates. If the owner does not agree with the amount of property tax, they can file an objection or appeal. Property tax can be paid by bank transfer, direct debit, or direct debit authorization.
For some time now, Germany has had the electronic register elster, which can be used to pay property tax online. Elster is a platform run by the Federal Central Tax Office, which taxpayers can use to submit their tax returns and make tax payments. Property tax can also be paid via Elster, which has the advantage that owners can make payments from home and do not have to adhere to the opening hours of banks or tax offices. However, owners must create a user account and register once to use Elster.
In Austria, incidentally, ImmoESt is crucial for sellers of real estate.
Homeowners should check their property tax assessment early on to ensure that the amount of property tax has been calculated correctly. If any discrepancies or errors are found, it is advisable to file an objection or appeal. This can be done either informally or using an objection form, which is available from the tax office or local authority. It is important that the objection is submitted within the specified time limit, as otherwise the opportunity to challenge the property tax may be lost.
Homeowners should also ensure that property tax is paid on time to avoid late payment interest and reminder fees. It is advisable to keep the property tax assessment carefully and note all payment dates in your calendar. Using Elster can also help you keep track of payments and pay property tax conveniently from home.
More Articles: